Everbe ransomware is a type of malware that appends .g8R4rqWIp9 or another extension to locked files and then demands a ransom for a decryptor
Everbe ransomware is a virus that locks up personal files and is now decryptable.

Everbe ransomware is a virus that locks up personal files and is now decryptable.
Everbe is a file locking virus that was released in March 2018 and since then has been reaching targets worldwide by using multiple attack vectors. Malware receives regular updates, although threat actors usually take around a month’s break before releasing a new variant. Initial versions appended .everbe or .eV3rbe file extension after performing file encryption with the help of AES + RSA encryption algorithms; then malicious actors used .embrace, .volcano, and many others. The most recent variant of Everbe ransomware that was spotted actively infecting users used .g8R4rqWIp9 marker, also known as Paymen45 virus.
As it is typical to ransomware, Everbe virus also leaves a ransom note behind, under such names as !=How_recovery_files=!.html, EVEREST LOCKER.txt, !#_How_to_decrypt_files_#!.txt, readme.txt, and many others. Over the years, the contents changed inside, providing a different contact email address.
So far, there are three major releases of malware, including Everbe 1.0, Everbe 2.0, and Everbe 3.0. While the two latest versions cannot be decrypted, all 1.0 variants can be recovered with the help of InsaneCryptDecryptor, available for free. Unfortunately, there is no guarantee that the tool will work for all victims, so we provide alternative methods for data recovery below.
| Summary | |
|---|---|
| Name | Everbe |
| Type | Ransomware |
| variants | |
| Encryption algorithm | Malware uses AES/DES to lock files and RSA is used for key encryption |
| Danger level | High. Makes system changes and encrypts files; demands a ransom |
| Ransom note | !=How_recovery_files=!.txt or !=How_recovery_files=!.html, readme.txt, and others |
| Appended file extension |
.[[email protected]].everbe; .[[email protected]].embrace; .pain; [[email protected]].eV3rbe; .[[email protected]].HYENA; .[[email protected]].thunder; .[[email protected]].neverdies; [[email protected]].neverdies; .[[email protected]].divine; .[[email protected]].EVIL; .[[email protected]].NOT_OPEN; .[[email protected]] .EVEREST; .[[email protected]].lightning; .seed; .[[email protected]].DEADMIN; .Oypl7T1i9; .[[email protected]].CULEX; .g8R4rqWIp9 |
| Contact email addresses | [email protected], [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], and many others |
| Data recovery | All variants belonging to Everbe 1.0 can be decrypted with the help of InsaneCryptDecrypter. |
| Malware removal | Do not attempt to eliminate ransomware manually but instead employ anti-malware software for the purpose – we recommend using SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes |
| System fix | If you face random crashes, errors, and other stability issues after malware elimination, scan your system with Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego to fix virus damage |
When the name is changed data immediately becomes compromised and unusable due to a sophisticated encryption algorithm. Everbe ransomware virus then generates a ransom note and spreads copies in all of the existing folders. This os just one of the examples, as ransom note contents differ with each Everbe virus versions:
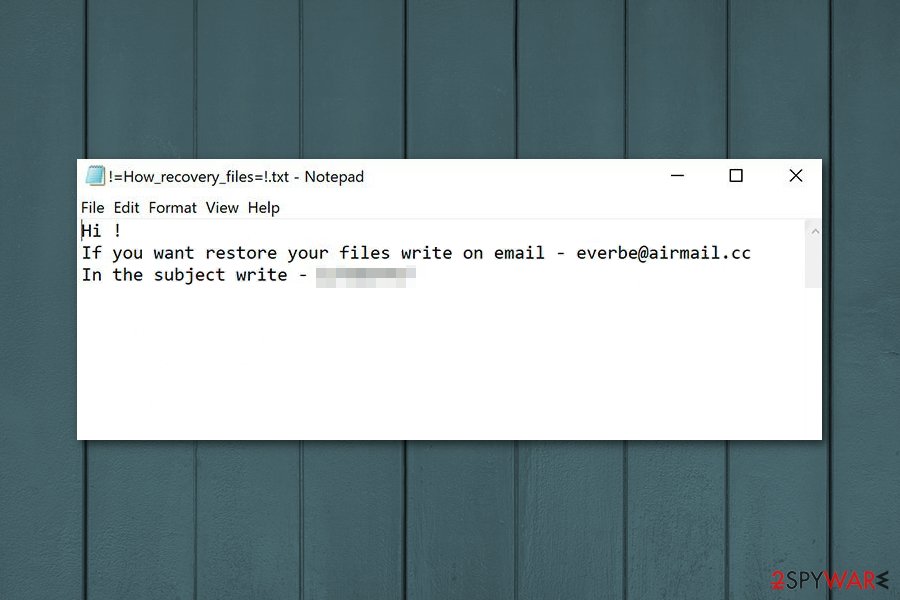
Hi !
If you want to restore your files write on email – [email protected]
In the subject write – [redacted victim ID number]
As you can see from the quote above, this short message encourages users to contact developers via [email protected] email, if they want to restore encrypted data. The ransom note also provides unique victim’s ID which is asked to enter in the subject line of the email.
However, we do not recommend contacting the creators of Everbe ransomware and following their instructions. There’s no doubt that they will ask Bitcoins or another cryptocurrency in exchange for unique decryption key created for each victim. But once cybercriminals receive the payment, they might disappear and leave you with a bigger loss.
No matter how much you need to get back your files, you should remember that there are no guarantees that crooks keep their promise and help with data recovery.[1] Additionally, paying the ransom gives no results in Everbe removal. Hence, your computer remains vulnerable and sluggish. Besides, there is a free decryptor available,[2] so there is no need to pay hackers.
Keep in mind that you need to remove Everbe ransomware first before you can proceed with data recovery. However, if you do not have backups, you can try using additional tools that we have presented at the end of the article. If they do not help, you should remain patient and wait for malware researchers to create a free decryptor. Finally, if your computer starts lagging and crashing after Everbe ransomware termination, you can make use of Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego to fix virus damage quickly.
Everbe ransomware is a file-encrypting virus that does not reveal much of the data recovery possibilities at first.

Everbe ransomware is a file-encrypting virus that does not reveal much of the data recovery possibilities at first.
Different Everbe family variants
The good news is that Everbe decryptor can help while dealing with two variants of malware — Embrace and Painlocker. Although, this only work for these firstly discovered ones because hackers are known to modify the code of ransomware so that decryptor would not work. These versions came out quickly one after another, each having a new name altogether.
Once more, two new versions came out in July 2018. Everbe 2.0 and Hyena Locker are not decryptable yet. The previous tool does not work. These two are similar and have lengthy ransom notes containing new contact emails (two for each version) and new file extensions.
Embrace ransomware
Embrace ransomware made a comeback as the first continuation of Everbe malware. It spread through unprotected RDP, using malicious attachments in spam emails or was injected into malicious websites. It used the same encryption algorithm (AES or DES) to lock up files and added [[email protected]].embrace. For example, a file called picture.jpg would be turned into picture.jpg.[[email protected]] .embrace.
The ransom note !=How_recovery_files=!.txt slightly differs from the first variant and urges users to contact hackers via [email protected]. Victims are also warned that in case the payment will not be made within seven days, the price of ransom will double. It is unknown how much money crooks ask for; however, prices usually range between $500 and $1500, and payments are executed in Bitcoin or another cryptocurrency.
As usual, we recommend users to ignore ransomware authors and remove Embrace virus from the machine ASAP.
PainLocker ransomware
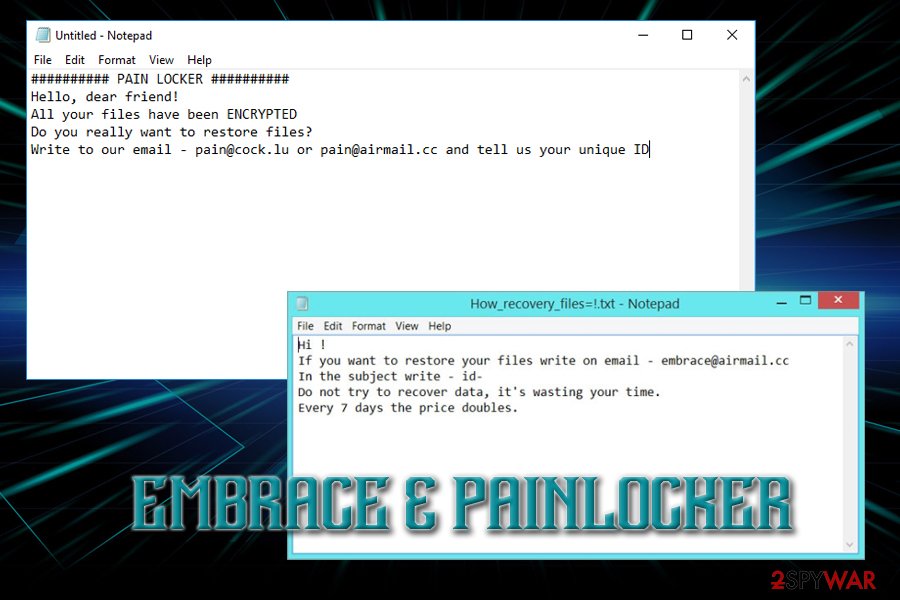
PainLocker is the latest addition to Everbe crypto-malware family. It adds [[email protected]].pain appendix to each of the files and generates ransom note of the same name – !=How_recovery_files=!.txt., which states the following:
########## PAIN LOCKER ##########
Hello, dear friend!
All your files have been ENCRYPTED
Do you really want to restore files?
Write to our email – [email protected] or [email protected] and tell us your unique ID
Painlocker wants users’ money. Thus, these hackers are not your friends (as they self-proclaimed)! Even though the decryptor works for this version of the virus as well, in rare cases it may not work for you. Therefore, it is vital to keep regular backups and employ reputable security software which could detect malicious threats and eliminate them before they can enter. If you found your files encoded, hurry up and remove PainLocker using an anti-malware tool.
Embrace & PainLocker – the newest versions of Everbe malware

Embrace & PainLocker – the newest versions of Everbe malware
Everbe 2.0 ransomware
This version came out in July 2018 as the second version to the main ransomware Everbe virus. Security experts were convinced that the virus will remain decryptable. However, decryption tools that have already been presented do nothing to recover files encrypted by this ransomware version. This variant is appending .[[email protected]].eV3rbe file extension or .[[email protected]].thunder appendix to the target data.
The particular version is using AES-256 encryption method. This version offers to test its decryption capabilities by decrypting three the most important victim’s files. The ransom amount is still unknown, so it is possible that the ransom you need to pay depends on the time you take to contact the criminals. However, we highly do NOT recommend contacting cybercriminals. Instead, you should try the data recovery steps given at the end of this post.
Hyena Locker ransomware
Hyena Locker is the fourth version of the ransomware which showed up in July 2018. It is using three-paragraph ransom note to suggest its victims sending files to test the decryption procedure. This is offered so you can believe that the payment you send to cyber criminals will guarantee you the full decryption of your files.
Hyena is using .[[email protected]].HYENA file extension while marking encrypted files and generates the key which is saved on a remote server which belongs to hackers. Just like Verbe 2.0, it is using AES-256 encryption chiper. The virus is still undecryptable.
.[[email protected]][email protected] file extension virus
On November 22 2018, the newest Eveerbe ransomware variant was discovered. This virus comes with a typical lengthy file extension – .[[email protected]][email protected]. This version encrypts users’ personal data using the RSA-2048 encryption algorithm and marks them with the mentioned marker.
Then it delivers a ransom message in the file named as the previous versions – !=How_recovery_files=!. However, it shows up as a program window on the screen stating about the encryption and suggesting to contact developers via [email protected] or [email protected]. You shouldn’t do so and remove this virus instead. Based on the detection rate, you can use Reimage Reimage Cleaner for the job.[3]
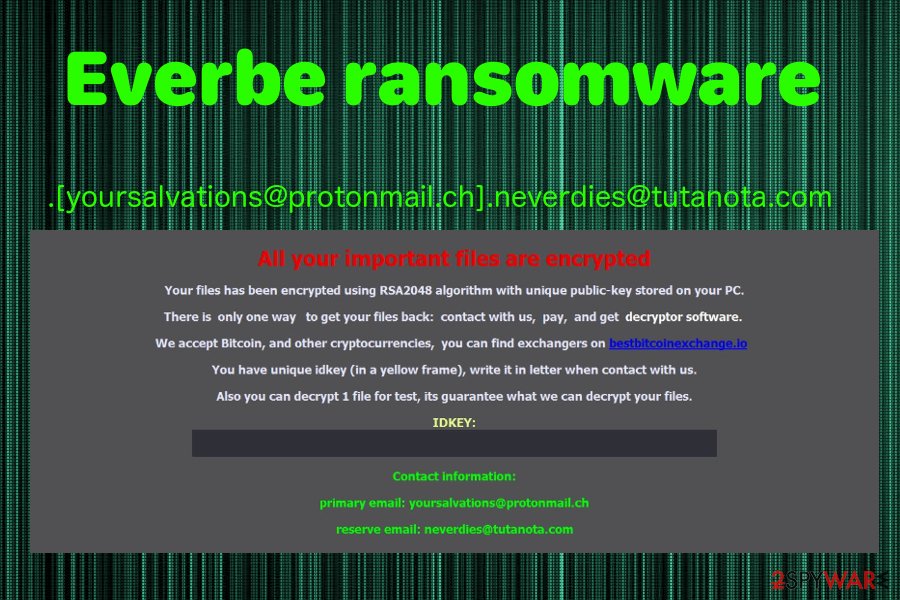
Everbe comes with the new file marker .[[email protected]][email protected].

Everbe comes with the new file marker .[yoursalvations@protonmail.ch].neverdies@tutanota.com.
Paymen45 ransomware, aka g8R4rqWIp9 ransomware
The release of Everbe ransomware was relatively successful to the attackers, as they followed with new variants at a regular pace. However, malware kept a low profile during 2019, just to come back in May 2020 with a new release Paymen45, more known as the g8R4rqWIp9 ransomware version.
Just as its predecessors, g8R4rqWIp9 ransomware uses several distribution methods to reach their targets, although if malicious actors are targeting organizations, they prefer using weakly protected Remote Desktop connections and brute-force attacks.[4]
Once inside the system, Paymen45 ransomware performs several changes to the Windows system and encrypts all data on local and networked drives. This way, PDF files, MS Office documents, databases, and other files are appended with .g8R4rqWIp9 extension, and can no longer be accessed. Once that is complete, users are asked to download the Tor browser and visit the http://paymen45oxzpnouz.onion/b241d8d739 address for further communication. As a backup means for contact, the attackers provide [email protected] email.
We do not recommend contacting or paying g8R4rqWIp9 ransomware authors, and instead of performing Paymen45 virus removal with anti-malware, and then using alternative methods for data recovery.
Macro-filled documents from spam emails distribute ransomware payload
The main way how ransomware is being spread on the web and installed on computers is spam emails.[5] They often include malicious attachments that execute download and installation of malware to your computer. Letters can be called like they are from real and big companies like PayPal, DHL, LinkedIn, and others.
Additionally, infected email attachments usually look safe to open. Creators of malware often inject malicious code into Word or PDF documents. In some cases, ransomware might arrive in the ZIP archive. So, you should be extremely careful with received emails.
Security specialists from NoVirus.uk[6] also warn that authors of malware might use other methods to spread the file-encrypting virus, such as:
- Unofficial software download sources or peer-to-peer networks that promote and offer to install suspicious programs;
- Fake updaters might include malware instead of being upgrading any software;
- Security pop-ups might ask to install fake security programs that are malware;
- Malicious ads placed on both legit and high-risk websites.
To avoid infiltration of such cyber threat, you should be not only careful with emails and learn how to identify tricky messages sent by hackers, but also follow major security tips, such as avoiding visiting potentially dangerous sites, downloading programs from ads or unauthorized download sites. Additionally, data backups and installation of antivirus program helps to minimize the risk of ransomware attack.
Eliminate Everbe immediately and clean the system
Everbe removal needs to be done using the anti-malware program. Ransomware creators upgrade their codes and make viruses more evolved each time the new version comes out. We recommend using SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner and Malwarebytes for cleaning your computer and then fixing damaged system files with Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego to avoid Windows reinstallation. However, feel free to use your beloved anti-malware program, but do not forget to update it first!
Additionally, ransomware virus can block access to the security program or its installation process. So you might need to do other steps that are mentioned in a removal guide below.
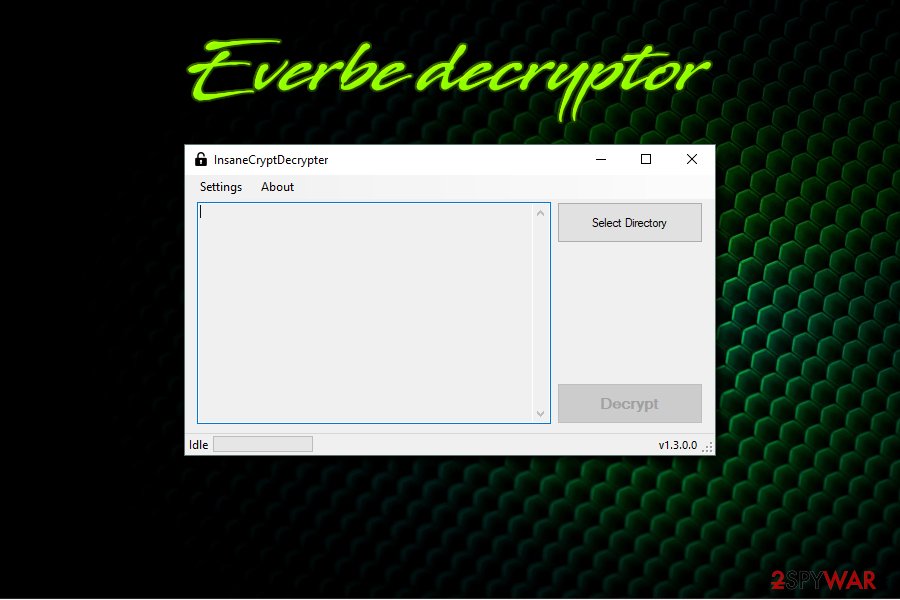

Once you remove Everbe from the machine, you can begin the data recovery procedure. You should first try to gain access to your files back by using Embrace Decryptor or InsaneCryptDecrypter. These tools should be helpful with almost every version of this ransomware. In case it does not work for you, below you can see other options for restoring your data.
This entry was posted on 2020-05-07 at 03:36 and is filed under Ransomware, Viruses.

