Locky is a threat known as a notorious ransomware virus because it relies on file-locking and ransom demanding for many years
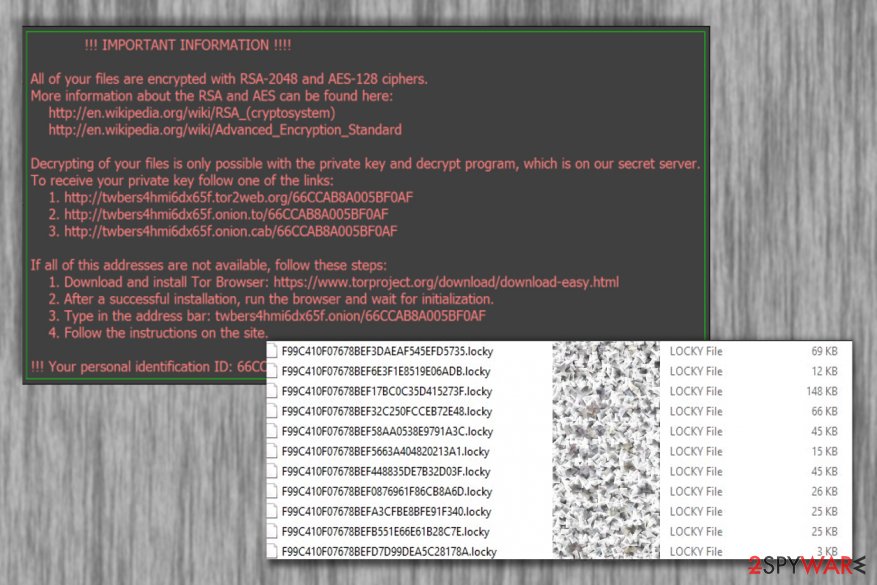

Locky is a seriously dangerous ransomware virus that encrypts data using RSA-2048 + AES-128 cipher with ECB[1] mode. The malware made the first appearance in February 2016, when developers sent out 500,000 phishing emails containing the malicious code. It affects victims to this day and malware researchers continue reporting about attacks and how the threat works.
Locky relies on strong techniques and enters the systems of targeted or ransom machines, so the nasty cryptovirus can get released. It spreads quickly and can be found in various regions across the world, including North America, Europe, Asia. The most affected countries of the attacks included the USA, Germany, Italy, Spain, and France. The initial extension the virus used for the encrypted files was .locky, but as the threat evolved, new extensions such as .asasin, .ykcol, .diablo6, .osiris, .odin, .thor, .zepto, .shit, .aesir and .loptr emerged. Asasin and Ykcol are the latest file extensions used by Locky virus.
In most of cases, the victims download the Locky ransomware to their computers themselves as a regular email attachment, typically, a Microsoft Word or Microsoft Excel file carrying an embedded script that gets executed if the macros are enabled. Then, the AES and RSA encryption algorithms come to play, followed by the addition of specific file extensions to the infected files. The file which provides data recovery instructions is called _Locky_recover_instructions.txt. It is saved on the computer’s desktop and opened each time the user tries to open any of the encrypted files.
This is powerful malware, so ransom payments can go up to tens of thousands for one victim. It is linked with a notorious hacking collective known as Dridex. These two can work together and gather payments from victims. Typical ransom demands for Locky virus range from 0.5 to 1.0 Bitcoin, roughly $4,000 to $8,000. If you have a BTC wallet on your computer, your funds can be at risk because malware may encrypt that. This infection is more complex than any other cryptovirus, so rely on professional tools and remove the virus ASAP.
| SUMMARY | |
| Name | Locky |
|---|---|
| Type | Ransomware |
| Encryption algorithm | RSA-2048 + AES-128 |
| First discovered | February 2016 |
| Countries infected | 105 |
| Variants | Locky-Zepto, Locky-Odin, Locky-Shit, Locky-Thor, Locky-Asier, Locky-ZZZZZ, Locky-Osiris, Locky-Loptr, Locky-Diablo6, Locky-Lukitus, Locky-Ykcol, Locky-Asasin |
| Ransom note | _Locky_recover_instructions.txt – the file that is delivered on the desktop and in other folders. Besides that malware sets the wallpaper to the same message |
| Ransom size | 0.5-1 Bitcoin |
| Biggest known payout | $17,000 |
| Distribution | Unprotected RDP, phishing emails, exploit kits, malicious websites, etc. |
| Extermination | Automatic only -use anti-malware tools and remove Locky ransomware fully |
While Locky was the biggest threat of 2016, experts are doubtful the virus will ever come close to its initial success. For example, the Hollywood Hospital in the US paid a ransom of $17,000 to recover invaluable files. Nevertheless, this does not stop the ransomware creators from trying. In June, virus researchers have detected a new variant of Locky spreading via a malicious spam campaign hosted by the Necurs botnet.
Unlike its predecessor, the malware currently infiltrates the machines running outdated and unsupported Windows versions such as Windows Vista or XP. Later variants are protected by Data Execution Prevention (DEP) which blocks the malware unpacker automatically [2].
The variants of the infection spread their malicious executable locky.exe via email, attached as a zip file labeled with random digits. Locky does not touch tmp, AppData, Program Files, Windows, and a few other folders, but encrypts the rest of the PC files with RSA-2048 and AES-128 ciphers. Eventually, the virus marks encrypted documents with .loptr extensions and drops a document called loptr-[random_4_chars].htm to list out the data recovery conditions.
Below is a table of the most frequent subject and attachment types[3]. As you can see, Locky developers even try to foist the infection under the disguise of a scanned file[4]. Note that the latest version of the threat is delivered under a fake of Microsoft Store in .7z folder instead of .rar and .zip[5].
The supposed sender writes under the name of Microsoft Store 2017. Even though Microsoft Store exists, the full credential of a representative is indicated in genuine emails sent (if sent at all!) by Microsoft company.
Table of subjects and attachment names used in Locky malspam campaigns
| Subject | Attachment name |
|---|---|
| – | services_[name]_[6 random digits].zip |
| – | [name]_addition_[6 random digits].zip |
| Payment_[date] | [name]_invoice_[6 random digits].zip |
| Scanned image from [printer model] | Scanned image from [printer model].png |
| PAYMENT | {17 digits}.rar |
| Voice Message Attached from {11 numbers} – name unavailable | {15 digits}_{7 digits}_{6 sigits}.rar |
| Microsoft Store E-invoice for your order #[number] | MS_INV_[random digit].7z |
| Emailing – CSI-034183_MB_S_7727518b6bab2 | July-August2017.rar |
| Status of invoice | [8 random chars-2 random chars].7z |
| Document invoice_95649_sign_and_return.pdf is complete |
The .7z attachment is broken: malicious emails |
Locky hit the web at the beginning of 2016[6] and has been continuously rotating its distribution techniques and functionality used to extort people’s money ever since. This volatility and unpredictability led Locky to become the first ransomware that made it to the top three on the most dangerous malware list.
Locky ransomware is a file encrypting virus that needs to be removed immediately. Please follow this guide.

Locky ransomware is a file encrypting virus that needs to be removed immediately. Please follow this guide.
Together with Conficker and Sality viruses, Locky hides behind 50 percent of all recognized malicious cyber attacks[7]. It is not hard to notice the fact that your device has been targeted by this parasite. The already mentioned file extensions .locky, .zepto, .odin, .shit, .osiris, .diablo6, .lukitus and .ykcol file extensions give it away.
If you happen to can see any of these extensions added to your scrambled files (see the picture below), you need to remove Locky virus first. Otherwise, it can try to continue its encryption on your computer. Besides, it can affect files that are in your network and similar locations.
For the removal of this ransomware damage and its files that get added in the system folders Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego. However, we must warn you that these programs cannot decrypt your encrypted files. Virus researchers are just in the middle of trying to find the “vaccine” for this version of ransomware. However, to recover the “locky datei” you can use Data Recovery tips created by 2-spyware.com researchers.
Distribution tactics used by the developers of the infamous ransomware
Ransomware, along with most of its follow-up versions, is mainly distributed via spam email attachments. It typically uses obfuscated HTA, JS, or WSF files which try to convince the victim that they contain some important files. The most popular one is called MRI6219316107.js. This JavaScript file is believed to be the main one used to install ransomware on the system. If you see this file attached to some suspicious email sent to you by an unknown person, delete such email immediately.
In the past, the ransomware used Word files to infiltrate the system without letting its victim know what is initiated behind his or her back. Besides, IT experts have also identified that the threat relies on .lnk files as well that are transferred to the affected system with the help of Nemucod. LNK file type represents Windows shortcuts and can be linked to an application that many people have on their computers, for example, Powershell.
The malicious .lnk file carries a Powershell script that connects to specific domains by using a parameter. The use of a parameter is a clear sign that criminals control these domains, and these malicious websites can be specifically prepared or just compromised ones held under control by cybercriminals. Researchers from Microsoft claim that malicious Internet sites are updated daily and are supplied with new versions of the malware payload.
The aforementioned PowerShell script is set to download the ransomware from predetermined domains. Typically, the malware is saved in the %TEMP% folder. The essence of using this technique is that the new .lnk file used helps Locky evade the detection of malware removal utilities. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to update security programs daily.
In the second half of June 2016, the infamous botnet called Necurs, which was believed to be shut down after a few weeks of existence, has re-emerged and started delivering updated Locky versions [8]. Unfortunately, but it seems that the botnet was actively used to spread this ransomware via infected email attachments, named: services_[name]_[6 random digits].zip, [name]_addition_[6 random digits].zip and [name]_invoice_[6 random digits].zip.
All these zip documents are loaded with the malicious JavaScript injection and leads to the infiltration of malware. After the victim opens this document, the malicious executable gets into the system and starts working. You have to perform a full Locky ransomware removal to get rid of it. 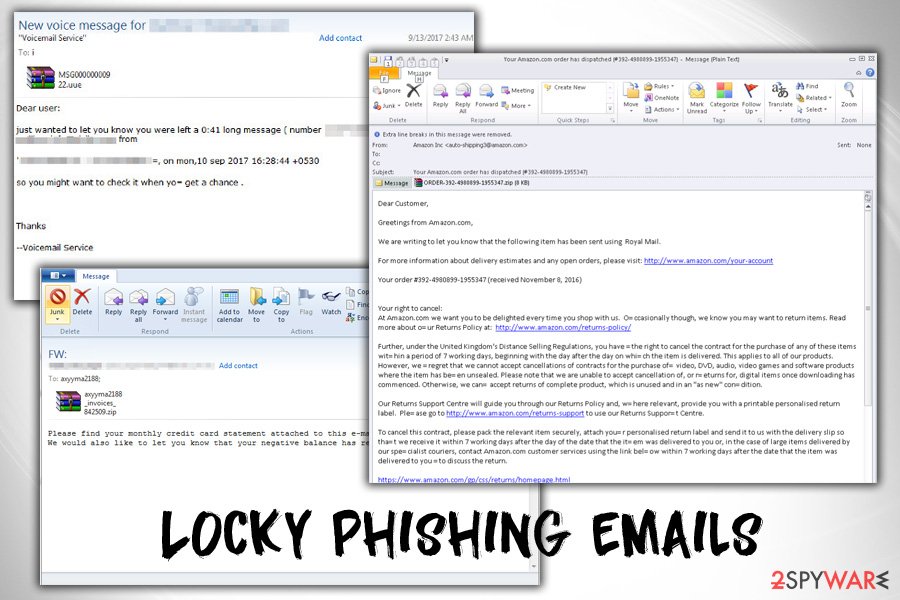
Examples of phishing emails sent out by hackers

Examples of phishing emails sent out by hackers
Get to know how the original Locky operates
When Locky was noticed for the first time, it seemed to work similarly to CTB Locker, Cryptowall, Teslacrypt, and Cryptolocker. Just like its predecessors, it used a mixture of RSA-20148 and AES-128 ciphers to leave its victim without any ability to retrieve his/her files. This combination of encryption ciphers can be beaten only with the help of a special decryption code which is held by the developers of malware.
In exchange for this code, victims are asked to pay from 0.5 to 1.00 Bitcoin (or $400). Nevertheless, security experts have been urging them NOT to pay for this key because there is no guarantee that the “key” will work for them. In addition, these commands can also be started by Locky malware:
- Once installed, the virus saves itself under svchost.exe name into %TEMP% directory. Malware also removed Zone.Identifier flag from this file to prevent the computer from identifying it as “File Downloaded from the Internet” and warning the victim. Then it executes this file.
- The virus assigns itself to startup programs, so that in case the victim restarts or shutdowns the PC during the encryption process or before it, it would still be able to finish the encryption procedure. It must be noted that this virus contacts its C&C center to get the unique encryption key.
- Data encryption begins. It might take several hours to encrypt the required files. As a rule, the virus stays unnoticed at this stage, but you may notice system slowdowns and similar issues on your computer.
- Now this ransomware starts showing a ransom note on victim’s computer. This _Locky_recover_instructions.txt warning message is almost identical to previous ones used to let people know how much bitcoins should they transfer to the developers of Locky virus for getting a special decryption key needed for the decryption of their files.
Cybercrime gang presents Lukitus – one of the most prevalent variants of Locky
Following the manner of its former versions, Lukitus variation showed up in the end of August 2017. It has been found spreading via mass mailing spam campaign initiated by Nemucod. It is believed that there are 23 million spam emails trying to infect users with Locky Lukitus. The corrupted email may arrive without subject or can use such words as Payment, Voice Message or Emailing – CSI-034183_MB_S_7727518b6bab2.
Note that in some email examples there are no official credentials provided below the sender’s name. Suppose if it were the genuine message, more information will be provided. If a victim dares to extract files from the [month-year].rar file, you will execute the further download process of the main payload of Locky malware.
Later on, the procedure becomes the same: the virus encrypts files and appends an enormous [first_8_hexadecimal_chars_of_id]-[next_4_hexadecimal_chars_of_id]-[next_4_hexadecimal_chars_of_id]-[4_hexadecimal_chars]-[12_hexadecimal_chars].lukitus file extension[9].
The malicious script is set to connect to remote compromised domains (including seoulhome[.]net, starsafety[.]net, grossert[.]de and others) and download malware from them. At the moment there are no tools capable of decrypting this virus.
This variation demands 0.49 Bitcoin. Considering the time span how long this particular virus has been on the cyber space, it would be naive to expect data recovery even after transmitting the money. Unfortunately, this variation is not decryptable yet.
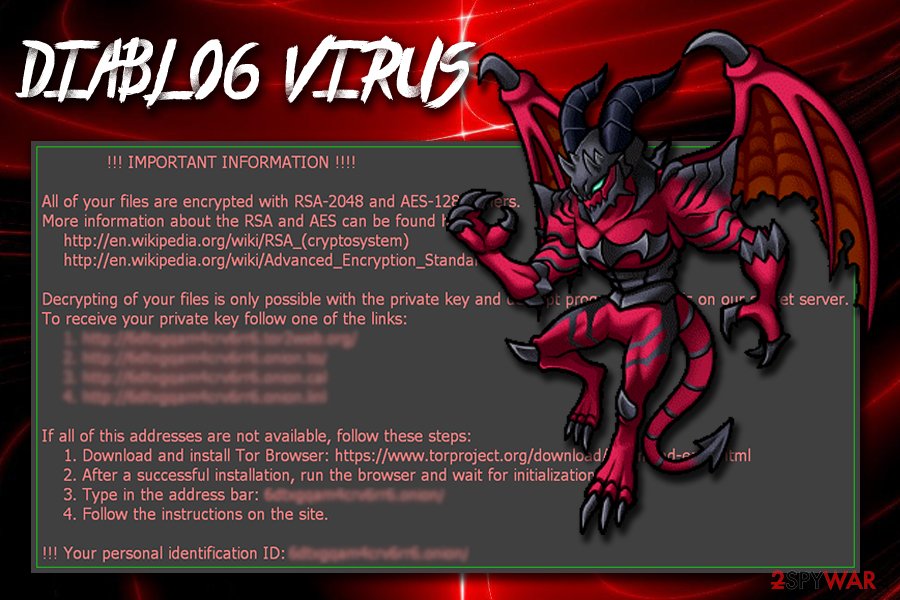
The comeback of Locky: Diablo virus
On August 9th, 2017, cyber security experts noticed a huge malspam campaign pushing the latest variant of Locky – Diablo ransomware. On August 8th, malware analysts spotted a test campaign. It is clear that ransomware developers were testing the virus before distributing it on a global scale. The following day Diablo6 started wreaking havoc worldwide.
The ransomware spreads via malicious emails with “E [date] (random digits).doc” in the subject line. The malicious email contains only a few lines of text, saying “Files attached. Thanks.” The email delivers a ZIP attachment called E [date] (random digits).zip.
Once the victim downloads and extracts the file, a VBS file drops on the system. If the victim opens it, the malicious code inside it connects to a remote server and downloads the ransomware.
The VBS file contains more than one malicious URL in order to ensure a successful delivery of the malicious payload. Once the file is downloaded, the script executes it instantly. Diablo6 then starts encrypting all of the victim’s data, adding .diablo6 file extensions on its way.
The ransomware creates a .HTM ransom note called identically as the virus and asks to download a Tor browser in order to access Locky Decryptor page. Here, the criminals suggest buying the decryption tool for half a Bitcoin.
Just a few days later after Diablo6’s debut, the virus’ authors changed its distribution tactics. The new malspam campaign now pushes PDF email attachments with embedded .DOCM files. The virus uses spoofed email addresses to trick unsuspecting victims into opening the attachment that is usually called as IMG_[4 random digits].PDF.
Launching the attachment gives the victim an option to review the contents of the file that are stored as a .DOCM file called identically as the PDF file. If the victim enables content (allows the use of Macros), the malicious code inside the document compromises the system by downloading and running a Locky Diablo6 virus on it.

The infamous ransomware breaks the silence and comes back with a new spam campaign
While the Internet community was cheering over the apparent halt in Locky ransomware distribution, its creators were actually plotting a new major spam campaign that would continue the legacy of this widely-dreaded threat. The security analysts have spotted new activity in Necurs botnet potentially associated with Locky around the middle of April.
After closer investigation, it was already confirmed that it’s actually Locky. The new spam campaign is now distributing the virus thousands of spam emails an hour. According to the latest findings, the subject line of the infectious emails features entries like “Payment Receipt 2724” or similar ones that appear convincing enough be taken for granted by the unsuspecting users and lead them to download the attachment file.
This virus has been using such deceptive techniques since the beginning, what has changed though, is how the virus gets executed on the computer. For that, the malware developers employ a technique used by the Dridex banking Trojan in its recent attacks. The malicious payload is now hidden within the PDF file with an embedded Word document inside which allows executing virus download via Word Macros.
Eventually, the encrypting parasite gets deployed on the computer in the form of a .txt file which later transforms to Locky’s executable redchip2.exe. If you see this file on your computer, do NOT interact with it, disconnect your computer from the network, and run an antivirus to locate and eliminate the malware.
The pace of Locky’s distribution slows down
While Locky’s attacks went during the holiday season, we can already see an increase in statistics – it means that criminals are back on track again and this time we want to inform computer users about another major and very dangerous email spam campaign that is going on at the moment.
As we have described earlier, Locky used to be distributed via .lnk files that executed Powershell scripts. This time, new Powershell scripts are created, and they are inserted into malicious .lnk files that are archived into .zip files and distributed via email.
Cybercriminals are trying to make an impression that these emails come from a well-known US Postal Service (also known as USPS). These emails contain a .zip attachment called Item-Delivery-Details-[random numbers].zip, Delivery-Receipt-[random numbers].zip, and similarly entitled files.
These emails contain a short message, which says that some kind of parcel has either been shipped/arrived/delivered and kindly suggests viewing contents of the attached archive. This .zip archive contains another .zip archive, which holds the malicious .lnk file.
Keep in mind that this .lnk file has double extensions – it has a fake “.doc” file extension added to its filename, although it doesn’t specify the file format at all. It is actually a .lnk file holding the PowerShell script. Once opened, the script gets activates and connects to obfuscated domains to download malware from them.
During this routine, the script performs checks to see if the download was successful and if the downloaded file takes more than 10kB in size. If so, it stops trying to download malware from these domains. It also stops if it goes through five URLs twice and doesn’t manage to download the ransomware.
What is interesting is that now cybercriminals decided to distribute Kovter.C Trojan alongside Locky ransomware. Therefore, if the PowerShell script successfully installs Locky, it then continues and connects to another malicious domain hosting click-fraud Kovter.C virus, which is known to be a file-less infection.
Virus’ developers add offline encryption feature
On September 2016 security experts noticed that Locky does not need to contact C&C servers to get the RSA Key (explained in step 2)[10]. Now it uses an embedded key what helps it infect computers having blocked C&C servers from passing through the Firewall. This new trick helps for the developers of this ransomware implement an offline encryption that does not require devoting their money for servers and domains.
However, it seems that this version of the virus hasn’t been perfectly polished yet, because there are some mistakes made related to its distribution. It appears that Locky, aka Zepto, virus arrives in the form of .ZIP file which contains JS files. If the victim attempts to launch any of them, a Windows Script Host error shows up. This message appears because these JS files are actually HTA files.
This version adds .Zepto file extension to encrypted files and creates ransom notes called _HELP_instructions.html and _HELP_instructions.bmp. At the end of September malware was discovered to rely on Quant Loader[11], a tool that is advertised in Russian underground hacking forums as a Trojan horse that is capable of infecting the victim’s PC without any harsh techniques and giving full access to the hacker.
Criminals who buy this Trojan can use a specifically designed admin panel that gives control of the compromised computers and allows to decide what malware to inject into them. Criminals can even choose what computers to attack, ordering them by geographic location.
According to research, Quant Loader malware is suspected to be one of the primary tools used to distribute Locky ransomware and also Pony Trojan (data-stealing virus). The distributors of Quant Loader are criminals that belong to the malware gang known as “C++ GURU” or “CPP GURU.”
The full list of Locky ransomware versions and related malware
Locky ransomware
Locky ransomware. It is the first version of Locky virus. It spreads in a form of Word document, which contains malicious code that can be activated via Word Macros.
Once the code gets activated, this malware downloads and executes a malicious program which scans the computer system for personal files and irretrievably encrypts them using AES encryption algorithm. It drops _Locky_recover_instructions.txt file on the computer after it encrypts all records.
This document informs the victim what happened and commands him/her to pay up to retrieve corrupted files. If your PC has been infected with Locky, you should not pay up! You risk losing your money since you cannot rely on cyber criminals and promises they make.
Unfortunately, computer experts haven’t found a tool that could decrypt files that ransomware affects, so the only possible way to recover your files is to import them from a backup. If you do not have one, there’s nothing much you can do now.
Locky decrypter
Locky decrypter, or Locky decrypt tool. It is a software that victim’s of this ransomware usually look for. Cyber criminals who spread this virus inform victims that the only way to decrypt the encrypted files is to buy a unique Locky decrypter software, which supposedly can decrypt victim’s data.
The price of this decrypter starts from 0.5 Bitcoins (which is equal to 225 dollars but may vary depending on the case. However, computer security experts encourage victims NOT to buy this software because it might be useless. We also advise you not to look for Locky decrypter on the web because cyber criminals can spread these files filled with malicious components.
AutoLocky virus
AutoLocky virus. This is a less dangerous copy of Locky virus. Its executive file spreads via spam emails and, once the victim opens it, virus encrypts files and asks for a ransom (0.75 Bitcoin, so approximately 325 dollars). It uses Locky’s name to look scary; however, it is not as dangerous as the real version of the malware.
AutoLocky ransomware is written in AutoIt language, so it is not as complicated as Locky, which is written in C++ programming language. Fortunately, computer experts have already discovered AutoLocky decryption tool, so now victims can recover encrypted files.
.locky file extension virus
.locky file extension virus. This variant of this ransomware appends .locky file extension to filenames after encrypting victim’s records. If you see that these extensions were added to your files, and if you cannot open them, it is a clear sign that you have become yet another victim of Locky virus attack.
This variant also suggests Locky decrypt tool in exchange for a large sum of money. As we have already mentioned, you risk losing your money just as you have lost your files if you transfer money to cyber criminals. We strongly advise you NOT to do so.
_Locky_recover_intstructions.txt
_Locky_recover_instructions.txt. This file includes Locky virus data recovery instructions. These are provided by cyber criminals, and unfortunately, they do not present information on how to recover files for free. This so-called ransom note or a few variants of it can be found on every computer that has been affected by this virus.
This document explains that victim needs to download and install Tor browser and then navigate to particular websites for further information how to decrypt Locky. Later on, hackers command the victim to buy and send Bitcoins to them.
Locky Bart virus
Bart virus. Also known as Locky Bart ransomware, this malware is considered unique since it does not encrypt files, but adds them to individual ZIP archives and protect them with a password. It names these archives as [original filename].bart.zip. What is more, this virus does not communicate with its Command & Control server, which means that it keeps locking files one after another even if the user disables Internet connection.
Another interesting feature of Bart is that it checks language settings on the computer and terminates itself in case Russian, Belorussian or Ukrainian language is set as default. This virus asks to pay 3 Bitcoins to get all data back. We never encourage ransomware victims to pay ransoms, as cyber criminals might refuse to provide the decryption key, or, in this case, Decryptor Bart.
Bart v2.0 ransomware
Bart v2.0 ransomware virus. A newly released and improved version of Bart ransomware is a serious menace for all computer users that do not keep their computers protected. After infecting the system, it encrypts records using RSA4096 encryption and adds .bart2.zip file extensions to them.
The virus demands roughly 1800 USD in exchange for the Bart2 Decryptor. Victims are advised not to pay such enormous ransom and look for other decryption methods. The most efficient way of restoring encrypted files is to import healthy data from a backup. Needless to say, Bart 2.0 removal should be fully completed before attempting to transfer data copies into the computer.
Zepto virus
Zepto virus. Zepto is the latest variant of an infamous ransomware. It was discovered in June 2016, and this virus is an improved version of the infamous .locky file extension virus. It was released right after Bart ransomware, and it spreads via malicious email campaigns.
This computer threat encrypts data using both AES-128 and RSA-2048 ciphers, making it nearly impossible to crack the virus and create a free decryption tool. In other words, it might be impossible to decrypt your files after this virus encrypts them. Authors of this virus ask to pay a ransom to get a Zepto decryption key, which can be bought via Locky payment site. However, there is no information if crooks actually provide victims with the key after they pay the ransom.
ODIN virus
ODIN virus. One of the latest versions of Locky can be recognized from .odin file extensions added to encrypted data and ransom notes left on the desktop – HOWDO_text.bmp, and HOWDO_text.html files. The virus commands the victim to go to the ODIN payment page, which suggests buying Locky Decrypter. Since this ransomware has not been defeated yet, so is ODIN, and victims can only hope for the best.
Files can be restored from backups, but Odin ransomware and related files must be entirely cleared from the system before plugging the device with the backup into the computer. Odin ransomware is just as dangerous as the vast of other crypto-Trojans and you must take actions to protect your computer in advance if you do not want to be affected by Odin’s payload.
Shit virus
Shit virus. This malware showed up in the beginning of October and shook the entire community with its name. Once it infects the target computer, it uses Rundll32.exe to start its work and drops _WHAT_is.html, _[random numbers]_WHAT_is.html, and _WHAT_is.bmp files to inform its victim about the computer’s state.
Beware that this malware targets over 380 file extensions, including docx, .xml, .txt, .pdf, .xls, .odt, .key, wallet.dat and others. It is essential to protect your computer from this ransomware because there is no Shit decrypter invented yet. To avoid such dangerous virus, you need to protect your computer with a powerful anti-malware software.
Thor virus
Thor virus. Thor ransomware has been detected at the same time when .shit file extension virus appeared. This new version adds .thor file extensions to each encrypted file and also distorts the original filename to make the files unrecognizable. It also leaves _WHAT_is.html ransom note and a .bmp version of it on computer’s desktop.
This particular ransomware version demands a slightly smaller payment – more or less half a Bitcoin. Unfortunately, there is no way to restore .thor files once the ransomware renders them useless. For this reason, victims are advised to protect files in advance by creating a backup and installing anti-malware software on the system.
Hucky virus
Hucky virus. Malware developers keep on using Locky as the software they base their own creations on. Hucky (an abbreviation of Hungarian Locky) is one of these products too. It has emerged on the web quite recently, so there is still not much information about it.
What we do know is that the ransom note and the desktop picture it deploys on the computer are all in Hungarian. So, the typical Locky file recovery instructions appear as _Adatok_visszaallitasahoz_utasitasok.txt and feature Hungarian data retrieval information as well. Another interesting feature is that Hucky ads the old “.locky” extensions to all of the encrypted files.
Though Hucky seems to replicate the older version of the Locky virus this does not mean it is less dangerous. We should not forget that it was the original Locky virus that has started spreading havoc on the unsuspecting victims’ computers. Thus, Hucky should not be treated any less seriously.
.Aesir file extension virus
.Aesir file extension virus. This virus emerged at the end of November 2016 and is yet another Locky’s version, which owns a name associated with Norse mythology. Following a successful data encryption using RSA and AES ciphers, .Aesir virus appends .aesir file extensions to encrypted data.
The new ransomware uses new C2 servers and is reportedly distributed via the malicious Facebook spam campaign that is based on bogus message attachment that ostensibly is a Photo_[random chars].svg file.
Once the victim clicks to open it, a hidden JavaScript code gets activated, and it redirects the victim to a phishing website, which asks to install a browser add-on in order to view a video. If the user installs it, the malicious extension downloads Nemucod Trojan downloader and sends out the malicious .svg file to all victim’s Facebook friends via FB Messenger.
As a result, the victim unwillingly delivers the malicious file to all friends and receives a Trojan that connects to the online server and downloads the Aesir ransomware virus to the computer. .Aesir ransomware is yet another undecryptable ransomware variant; the only ones who can recover encrypted data are those who have an intact data backup. The virus must be removed from the system before plugging the backup drive into the PC.
Osiris ransomware
Osiris ransomware virus. Spotted on December 4th, the new Locky virus shows its uncrackable power to render the victim’s files useless again. Currently, the malware spreads around in the form of an obfuscated .zip archive that features a .vbs file.
Malicious emails that deliver the malicious program reportedly named “Photo/Document/Archive from office.” After encoding all victim’s files, the malicious program appends .osiris file extension next to the original file name and drops a ransom note called OSIRIS-[4 symbols].html in every folder that holds encrypted records.
Just like previous versions, Osiris virus uses an uncrackable encryption method and obfuscation layers to prevent malware researchers from finding an antidote for it. Currently, there is no information whether the decryption software offered by malware authors actually can decrypt files, so victims are advised not to rush to buy the decryption software.
Besides, criminals might refuse to provide it – we know cases when ransomware authors pretend to be negotiating with the victim but ask for more money as soon as the victim transfers the smaller ransom to criminals.
Our team recommends victims to remove Osiris as soon as possible because the malware might download additional viruses to the system while the victim hesitates whether to pay the ransom or not.
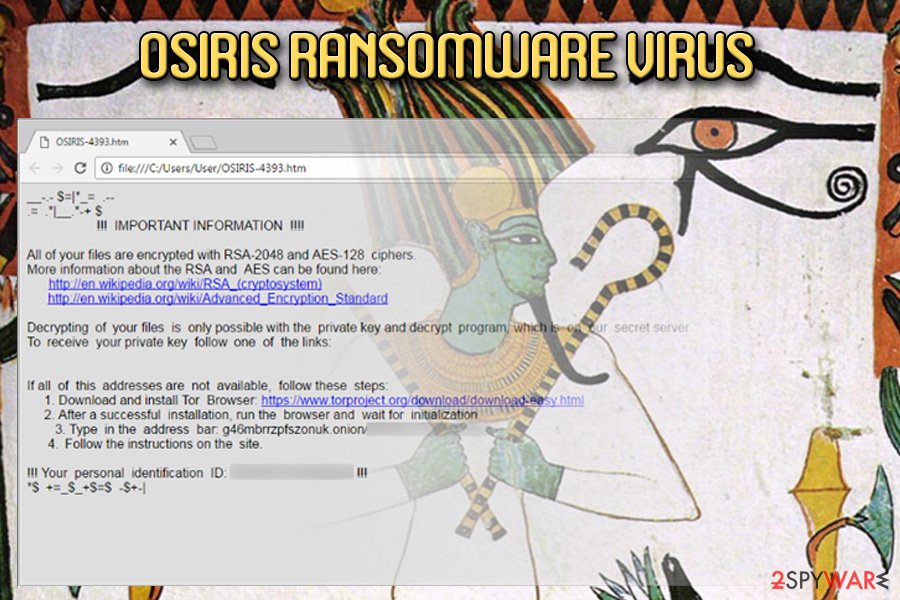
This version of malware drops a ranom note called OSIRIS[4 digits].html.

This version of malware drops a ranom note called OSIRIS[4 digits].html.
Locky Impersonator virus
Fake Locky ransomware (Locky Impersonator virus). Considering that Locky is a fearsome word to anyone who is at least a bit familiar with cybercrime news, amateur virus’ developers try to get their piece of the pie trying act on behalf of the real Locky virus. The latest fake Locky ransomware is known as Locky Impersonator ransomware, however, its authors obviously lack programming skills because they didn’t even bother to create payment website for victims to pay ransoms.
Instead, they count on way easier tactic and leave a ransom note called Rans0m_N0te_Read_ME.txt on the compromised computer’s desktop, filled with commands from cybercriminals. The ransom note says: “Files has been encrypted with Locky Ransomware […] nobody will be able to recover your data since its set to AES-256 and requires our Key“.
Locky Impersonator demands 1.0 BTC sent to a provided Bitcoin wallet address and says that if the victim fails to pay up within 48 hours, the ransom price doubles. In case the victim doesn’t transfer money in 72 hours, crooks promise to delete recovery keys.
They also ask the victim to contact frauds via [email protected] email address. We highly recommend you to remove Fake Locky virus and patiently wait for a free decryption tool, which malware experts can create anytime soon.
Diablo6 ransomware
Diablo6 ransomware virus. It is the latest variant of Locky ransomware that encodes files with RSA-2048 and AES-128 and appends .diablo6 extension to filenames. Consequently, the content of files becomes unreadable.
The virus is currently being pushed via two massive malspam campaigns. The virus arrives in a ZIP file that contains a VBS downloader. Once executed, the VBScript connects to one of the malicious URLs and downloads the ransomware to the computer. The VBS file is also responsible for launching the ransomware.
Another malspam campaign pushes PDF attachments with embedded .DOCM files that contain a malicious Macros script. Once executed, the compromised document downloads malware from an infectious domain and runs it on the target computer.
The virus renames original file names using victim’s ID and random characters in such way: [eight first characters of the victim’s ID]-[next four characters of the ID]-next four characters of the ID]-[four random characters]-[twelve random characters].diablo6. Following a successful encryption, the ransomware creates diablo.htm (the ransom note) and diablo.bmp (it sets this image as desktop’s wallpaper).
The ransom note commands the victim to install Tor browser and access a website that contains data recovery instructions. The .onion website states that the victim has to pay 0.5 Bitcoin to restore encrypted data. Unfortunately, it is unknown whether criminals actually restore the victim’s files after receiving the ransom.
Besides, we do not suggest you motivate the frauds by paying them. We highly recommend you to remove Diablo6 and try to recover your files using methods described in the data recovery section below the description of this virus.
Lukitus ransomware
Lukitus ransomware virus. Lukitus ransomware variant emerged and was used in cyber attacks starting from mid-August to 18th of September. The malware dropped lukitus.html and lukitus.bmp files to explain to the victim how to transfer money to extortionists and collect the decryption software that supposedly can recover lukitus files.
One of the latest Locky’s variants used to demand half a Bitcoin from victims. Criminals use this malicious software as an extortion tool that damages victim’s files using a combination of RSA and AES encryption algorithms. So far, no one managed to break the encryption used by this malicious virus and is unlikely to do so in the future.
Lukitus ransomware was actively distributed via the Blank Slate campaign that was also used to push Cerber, GlobeImposter and Gryphon ransomware viruses. The activity of this virus was extremely active; however, the number of victims dropped as soon as Ykcol virus appeared.
Ykcol ransowmare
Ykcol ransomware virus. August 18th, 2018 denotes the date of Ykcol ransomware appearance. This new malware sample uses a reversed name of Locky ransomware and obviously belongs to the infamous ransomware group.
The technical details of this new virus show that attempts to decrypt .ykcol file extension files using third-party data recovery software will likely be hopeless. The frauds who created the ransomware, unfortunately, are the only ones that can recreate encoded files. However, they only agree to do it after receiving a ransom from the victim.
Ykcol virus is currently distributed via massive email spam campaign that delivers messages with “Status of invoice” subject. The deceptive letter contains an attached 7z file. Once extracted, the archived file drops a VBS script on the system. This VBS file is entitled using a random set of digits.
If the victim opens the file to see its contents, the code inside of it will be activated and will perform the work of a malware downloader that connects to a remote domain, downloads Ykcol sample and runs it on the victim’s computer.
It is essential to remove Ykcol virus to continue using your computer after the ransomware attack. Remember – security programs aren’t designed to recover your files. In fact, data recovery is possible only in case you have a data backup. If you do not, chances to restore the encoded files are close to zero.
Asasin ransomware
Asasin ransomware virus. Asasin virus is the latest variant of the disastrous computer virus known as Locky. Modus operandi of the new variant hardly differs from the previous versions as it encrypts all data on the computer, drops asasin-[4 random chars].htm, asasin.bmp and asasin.htm files for the victim changes desktop background and demands a ransom.
Malware researchers have spotted a massive malicious spam attack at the night of October 10, 2017. A quick analysis of the files attached to malicious emails showed that they are designed to execute the latest Locky variant dubbed Asasin virus. The attachment of the deceptive email is a .HTML file which contains an iFrame tag including a link to a malicious .js file.
The JavaScript file gets into the computer system and an unsuspecting victim risks opening it since it looks like a regular document called Invoice_[random_chars].js. As we can see, Locky’s developers are playing with the “invoice” theme again as it probably convinces a lot of people to launch a malicious file without thinking.
Once executed, the JavaScript file connects to a remote domain, downloads and executes Asasin ransomware which then encrypts all data on the target system without any delays.
However, some researchers claim that the malspam campaign isn’t so successful as part of the emails contain a broken attachment that appears as a block of 64-encoded text. Therefore, the victim simply cannot open the attachment. Emails containing the broken attachment usually have Document invoice_95649_sign_and_return.pdf is complete or similar subject line.
Just like the previous versions of the fearsome computer virus, the new ransomware was entitled after the file extension it appends to crippled files – .asasin. The malware demands 0.25 Bitcoin in exchange for the Locky decryption key, although there is no news whether victims who decided to pay received the decryption solution. We strongly advise you NOT to pay the ransom.
Identify malicious emails before they trick you into opening a ransomware file
It seems that the virus’ developers turned back to the old distribution technique and again they use massive email spam campaigns to spread the malware. Millions of email accounts have received a message from scammers that feature such subject line:
Document/Photo/Scan from office
Such malicious electronic letter contains a .zip attachment that contains a .vbs file. If the user extracts the archive and launches .vbs file, it connects to one of dozens of malicious domains online and downloads Locky from there.
The virus arrives in an obfuscated form (with the help of XOR cipher with M7meLUMMVmEaR2eHds9aMc04MzRpdZmV value). Following successful infiltration, the malicious program gets decoded on victim’s computer and runs itself to start the encryption process.
What is more, this virus’ version also connects the compromised PC into a botnet[12]. It means that the compromised computer becomes a zombie that can be used for malicious purposes, for example, to implement DDoS attacks.
Questions & Answers about the data-destroying malware variant
Question: Can I decrypt my files after the infiltration of Locky virus?
Answer: Unfortunately, but there is no Locky decrypter invented yet. If you can’t remember backing up your data, which is the only process capable of helping people to prevent the loss of your files. However, there is no guarantee that anti-malware programs will help you to get your files back to you. Also, you should not forget the security of your computer. You must remove Locky virus from the system ASAP. For that, we recommend installing Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego.
Question: I have just received an email message saying “Please see the attached invoice”. Also, it has the “ATTN: Invoice J-98223146” document added to it. Unfortunately, I have already downloaded it, and now my files are blocked! Why?
Answer: Unfortunately, you were infected with .Locky virus. This is a seriously dangerous virus, which requires a special payment for giving people an opportunity to decrypt their files. To fix your computer and remove malicious files, please check the step-by-step guide given down below.
Question: How could I remove Locky virus? Will this help me recover my files that are blocked by this ransomware?
Answer: Unfortunately, but the easiest way to “unlock” your files is to enter the key, which is held by Locky developers. This key cannot be guessed or stolen, so the only option you have while trying to get it is to pay the ransom for its developers. However, you could try to recover your files with the help of their backups.
Check your CDs, external drives, Dropbox and similar online solutions for them. To remove Locky virus from your computer, you should install a reliable anti-spyware and check your computer for malicious files with its help.
Get rid of the shady Locky ransomware
In the past security software has often been failing to protect users from such ransomware-type threats, but now it seems that this issue is solved. Security vendors, e.g. Malwarebytes or SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner, have stepped up their game in the field of ransomware-fighting and the antivirus utilities have now become irreplaceable tools of blocking the threat and executing Locky ransomware removal before it causes further damage to the system. If you want to be safe from this virus, consider installing a reliable anti-spyware.
We should once again point out that Locky ransomware virus is a well-structured malware, which can easily lead you to the loss of your files. It is known that it has already been translated into a number of different languages and spread through Outlook and Microsoft 365. Some of the PC security experts call it “a masterpiece of criminality.” The consequences for the infected users can be devastating.
You must be extremely cautious when downloading attachments received from suspicious sources. No matter how harmless the sender of .js or word attachment seems, you should try to contact him or her before downloading it to your computer. If you are infected, you will soon realize that it’s not that easy to remove Locky, not to mention, recover the affected files.
In this case, the most important thing is to understand that the Locky removal does not help retrieve files that are blocked by this ransomware. If you are infected, you should follow a guide, which is given below, and fix your computer before you lose more of your files.
This entry was posted on 2020-05-22 at 09:01 and is filed under Ransomware, Viruses.

